A personal loan is a fixed-payment installment loan that can help cover major expenses or consolidate debt—often providing more predictable repayment than revolving credit.
Installment loan with fixed monthly payments—the most common personal loan structure.
Repayment terms often range from 12–84 months depending on lender and borrower profile.
Disbursement timing varies based on verification, processing, and lender requirements.
Many personal loans are unsecured; some secured options may be available to reduce risk.
Debt consolidation, major expenses, home improvements, and medical costs are typical applications.
Longer loan terms can increase total interest cost even if monthly payments seem lower.
A personal loan is financing issued to an individual that is repaid in fixed monthly installments over a defined term. Unlike revolving credit, personal loans generally have:
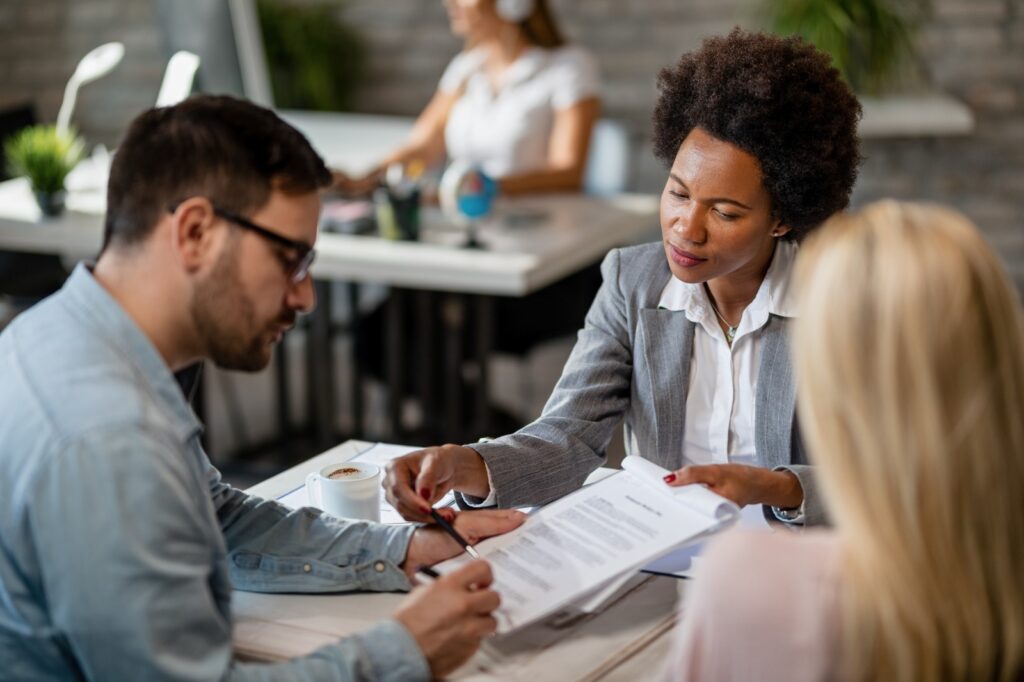

Replace multiple payments with one predictable fixed monthly payment.
Fund renovations or projects with structured, predictable budgeting.
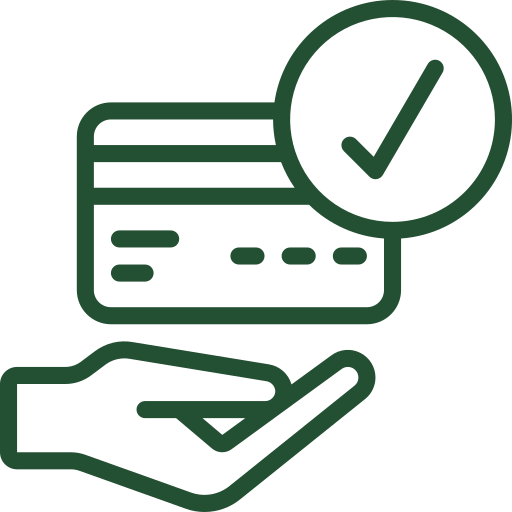

Cover planned or unexpected medical costs responsibly.

Appliances, furniture, and other one-time essential expenses.

Cover deposits, transport, and setup costs efficiently.

Access funds for urgent situations if payments can be managed
Lenders evaluate your ability and willingness to repay using several factors:
Includes credit score, payment history, delinquencies, collections, and utilization to assess repayment reliability accurately.
Compares total monthly obligations against income to determine ability to handle additional loan payments responsibly.
Lenders review paystubs, bank deposits, and tax documents, especially for self-employed applicants, to confirm earnings.
Considers job tenure and consistency of income over time to evaluate financial stability for repayment.
Assesses requested loan amount relative to borrower’s budget to ensure manageable repayment without financial strain.
Evaluates overdrafts, cash flow volatility, and account history, sometimes influencing lender’s willingness to extend credit.

APR / Interest Rate: Check whether fixed or variable; affects total repayment
Check if fixed or variable, as it directly affects total repayment cost.
One-time fees charged by lender for processing personal loans.
Penalties incurred when a scheduled loan payment is missed or delayed.
Some loans charge fees if you repay the balance earlier than scheduled.
Focus on total repayment, not just monthly amounts, avoiding surprises.